Imagine a notebook where every time someone gives money to someone else, it is written down, and everyone in your class gets an exact copy.
If someone tries to cheat and change a line in their book, everyone else's copies would show the edit. That is basically what blockchain is: an un-cheatable digital ledger shared by millions of computers. It is the powerhouse technology behind things like cryptocurrency, but it might change a lot more than just money.
Most people think blockchain is just a fancy word for Bitcoin, but that is not quite right. Bitcoin is like a specific brand of car, while blockchain is the engine that makes the car move. This engine is so powerful because it solves a problem humans have had for thousands of years: how do we trust each other when we do not know each other?
In the old days, we had to trust a middleman, like a bank or a government, to keep track of our money and records. They held the only notebook. But with blockchain, the notebook is everywhere at once. This is called decentralisation, and it means no single person or company is in charge.

Imagine you and your friends are playing a massive online game. Instead of the game company keeping track of who has the legendary swords, every single player's computer keeps a record. No one can 'glitch' the game to get extra items because everyone else's record would say they're cheating.
How the Chain Actually Works
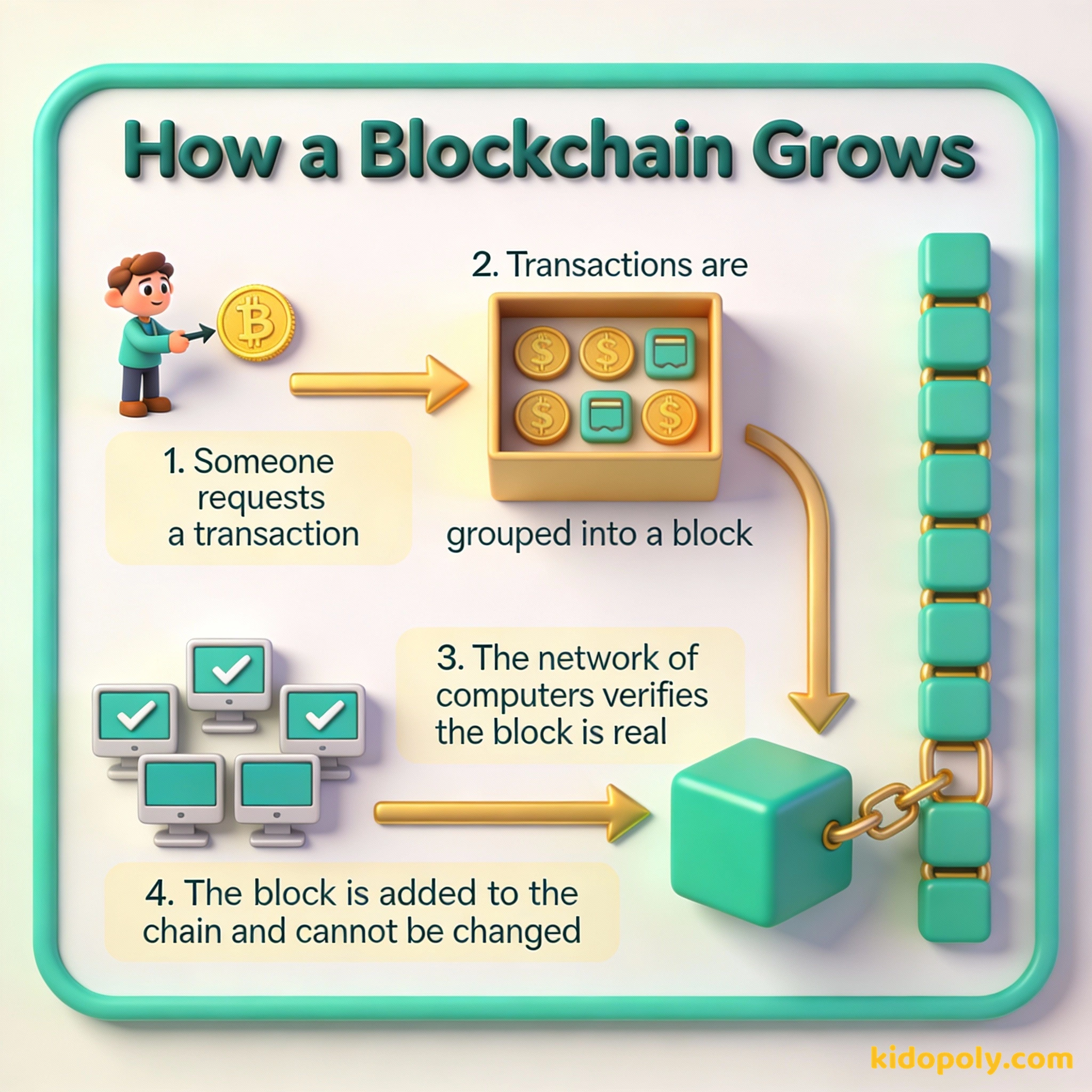
To understand blockchain, you just need to look at the name. It is literally a chain of blocks. Each block is like a page in our shared notebook. It contains a list of transactions, like "Person A sent 5 coins to Person B."
Once a page is full of transactions, it gets sealed shut and linked to the page before it. This link is very special. It is like a digital fingerprint that changes if even a single letter on the page is altered. If you try to change page 1, the fingerprint changes, which means the link to page 2 breaks, and then the whole chain falls apart.

Finn says:
"So if I try to delete the part where I spent my money, every other computer would basically yell 'Hey! That's not right!' and block me?"

Blockchain is a way for people who don’t know or trust each other to create a record of who owns what.
The Power of the Network
How do we know the information in a block is true? This is where the network comes in. Instead of one banker checking a list, thousands of computers around the world look at the same block at the same time. This process is called consensus.
They check to make sure the person sending money actually has enough to spend. If the majority of computers agree the transaction is real, the block is added to the chain. Because there are so many computers checking the work, it is almost impossible to trick the system.
Why It Is So Secure
If you wanted to hack a traditional bank, you would only need to break into the bank's main computer system. But to hack a blockchain, you would have to hack more than half of all the computers on the network at the exact same time. On big networks, that would mean hacking millions of computers at once.
This makes blockchain one of the most secure ways to store information ever invented. It creates a permanent record that is transparent, meaning anyone can see it, but immutable, which is a fancy word for "cannot be changed."

The very first block ever created on a blockchain is called the Genesis Block. It is like the first page of the world's most secure book.

The first generation of the digital revolution brought us the internet of information. The second generation is bringing us the internet of value.
More Than Just Money
While blockchain started with crypto-basics, people are finding amazing new ways to use this "un-hackable notebook." It is not just about digital coins anymore. It is about proving who owns things in the digital world.
- Digital Art: Artists use blockchain to prove they created a digital painting and to track who owns it. This is often called an NFT.
- Voting: Imagine voting for your school president on your phone, knowing that no one could ever lose your ballot or change your vote.
- Food Safety: Supermarkets can use blockchain to track where a head of lettuce came from, all the way back to the specific farm and the day it was picked.
- Medical Records: Doctors could share your health history securely so that you get the right treatment, no matter which hospital you visit.

Mira says:
"Exactly! It's like the whole world is keeping each other honest. It's not just a computer thing, it's a 'truth' thing."
The Two Sides of Blockchain
Even though blockchain is revolutionary, it is not perfect. There is a big debate about how it affects our planet. Some blockchains require a massive amount of electricity to power all those computers checking the transactions.
To take control of a major blockchain, a hacker would need more than 51% of the network's computing power. If a network has 1,000,000 computers, a hacker would need to control 500,001 of them. The cost to do this would be billions of dollars, making it much more expensive to cheat than to just play by the rules!
However, technology is moving fast. Newer versions of blockchain are being built that use 99% less energy than the original ones. Engineers are constantly working to make the system faster and cleaner so it can be used for everything in our daily lives without harming the environment.
The network is incredibly secure because so many computers are working, but it can use as much electricity as a small country.
Newer systems use 'Proof of Stake' which cuts energy use by 99% while still keeping everything safe and fast.

What the internet did for communications, blockchain will do for trusted transactions.
The Future of Trust
We are still in the early days of this technology. It is like the internet in the early 1990s. Back then, people thought the internet was just for sending emails. They had no idea it would eventually be used for streaming movies, ordering pizza, and attending school online.
Blockchain might do the same thing. By making it easy for people to trust each other without a middleman, it could change how we buy houses, how we prove our identity, and even how we interact on social media. Understanding it now gives you a head start on the digital world of tomorrow.

Finn says:
"I like the idea of tracking lettuce back to the farm. No more mystery salads!"
Want to see how consensus works? Grab three friends and four pieces of paper. Everyone write 'Finn gives Mira 5 stickers' on their paper. Now, try to secretly change your paper to say 'Finn gives Mira 100 stickers.' Show everyone. Since 3 out of 4 papers say 5 stickers, the group 'rejects' your fake version. That's blockchain!
Something to Think About
If you could create a record that could never be changed or lost, what would you use it for?
Think about things that are important to you, like your grades, your game achievements, or a promise you made to a friend. There is no right answer, but it helps you see why permanent records matter!
Questions About Investing
Can a blockchain ever be deleted?
Is blockchain the same as Bitcoin?
Who invented blockchain?
Your Journey Into the Future
Now that you know how the 'un-cheatable notebook' works, you're ahead of most adults! Blockchain is a big part of the future of money. If you want to see how this technology is used for actual coins, head over to our page on what-is-bitcoin to see the first-ever blockchain in action.

