1How Robots Recharge and Refuel
Just like you need a healthy breakfast to start your day, robots need a steady supply of energy to function! Most of the robots we see in our homes, like vacuum cleaners or toy drones, rely on lithium-ion batteries. These are the same kinds of batteries found in your tablet or phone. Some smart robots are even programmed with "auto-docking" technology. When their power level drops below 15%, they use infrared sensors to find their way back to a charging station, plugging themselves in for a "robot nap" so they can wake up ready to work again!
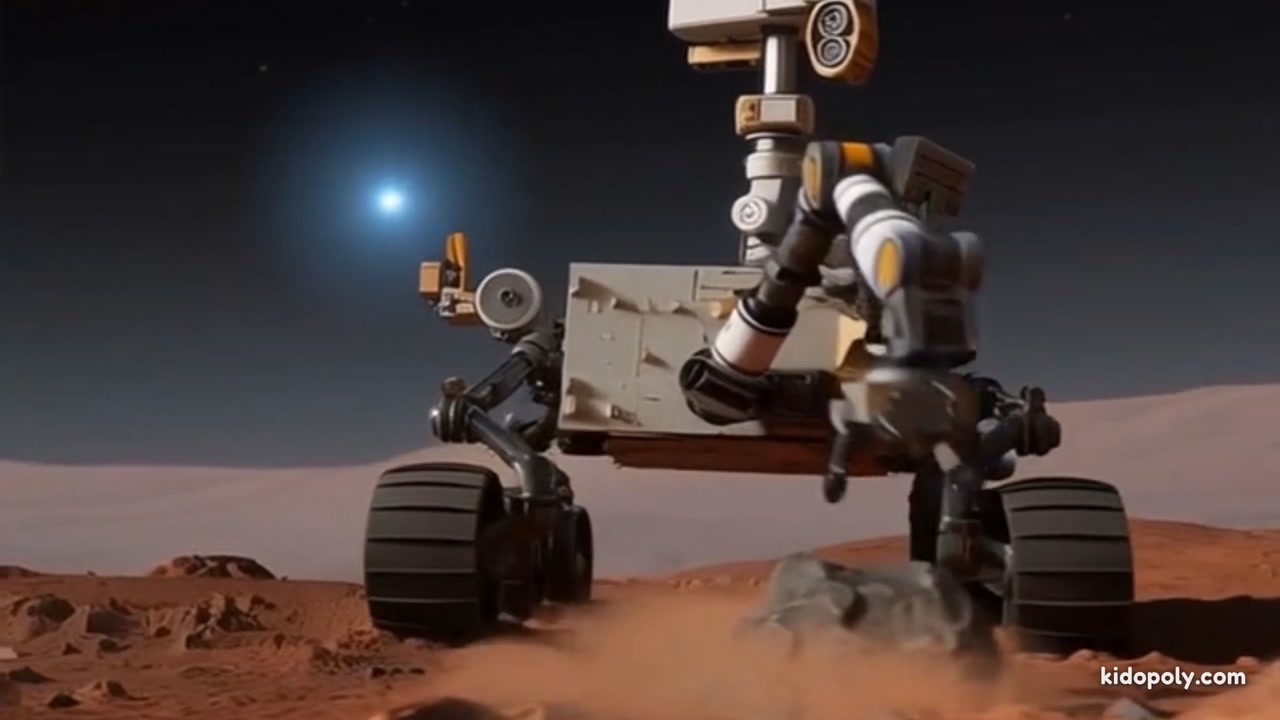
2Solar Power for Space Explorers
When robots travel to places where there are no wall outlets, like the dusty surface of Mars, they have to get creative. Space rovers are often covered in shiny solar panels that act like high-tech leaves. These panels catch photons from the sun and convert them directly into electricity. This allows a robot to survive for a very long time—sometimes over 10 years! However, solar power can be tricky; if a dust storm covers the panels or the sun goes down, the robot has to use energy it stored in its batteries during the day to stay warm through the freezing Martian night.
3Deep Sea Tethers and Fuel Cells
In the deepest parts of the ocean, it is pitch black, meaning solar panels won't work. To solve this, scientists often use "tethers." A tether is a super-strong cable that can be over 3,000 meters long! It acts like a giant extension cord, sending electricity from a ship on the surface down to the robot. For robots that need to move more freely, engineers use fuel cells. These are like tiny power plants that mix chemicals, such as hydrogen and oxygen, to create electricity without needing to be plugged in. This tech allows robots to explore shipwrecks and underwater volcanoes for days at a time.